ROH and ROH Profiles
Runs of Homozygosity (ROH) are contiguous regions in the genome where an individual has inherited identical genetic segments from both parents. The sum of all ROH regions gives the genomic inbreeding coefficient (GIC).
For details about ROH, please visit our lexicon article: ROH.
In the individual assessment, the ROH are displayed as an “ROH profile”.
The profile shows in the best possible display resolution where the various ROH regions are located in the individual chromosomes and how large they are.
In populations with low general inbreeding, the ROH profile can be the first indication of whether the animal being examined is the result of mating between close relatives (parent-child, full siblings). In breeds with pronounced general inbreeding, all chip markers must be evaluated to obtain this information.
Examples for ROH Profiles
The ROH profile of an evaluation is part of the online animal record in the “Inbreeding and Diversity” section.
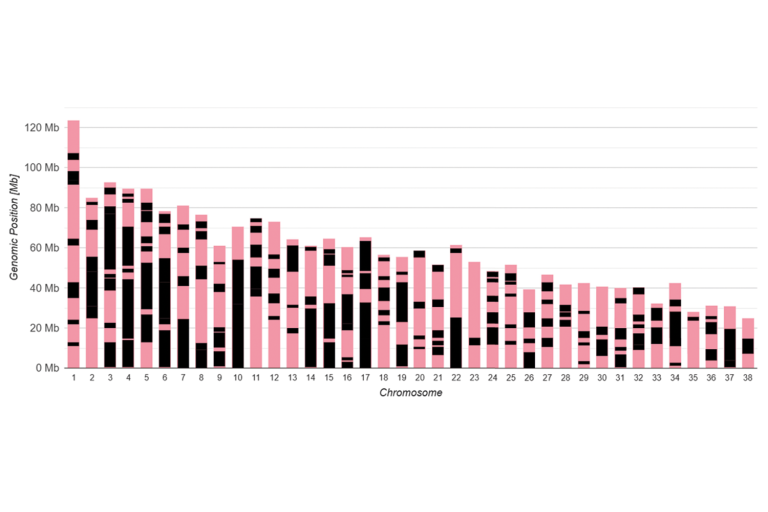
The ROH profiles of two dogs are shown as examples:
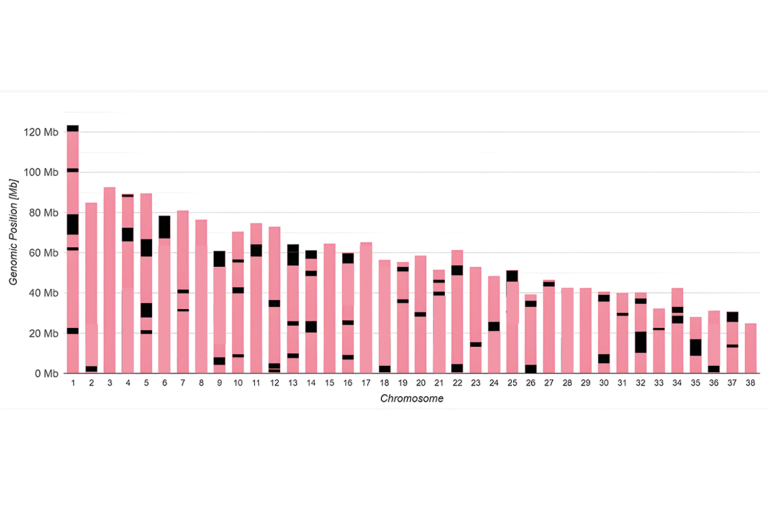
The image shows a a dog with a genomic inbreeding coefficient of over 40%.
This level manifests when related individuals are mated over several generations.
IMPORTANT: Such values are also found in dogs that, according to pedigree calculations, have no common ancestors in recent generations (IC = 0)
The display option used in the examples shows the ROH in terms of extent and location on the individual chromosomes:
The pink bars represent the chromosome pairs (excluding sex chromosomes) in their total extent (dog = 38 autosome pairs).
The black areas layered above them are the ROH.
Further display options can be selected in the animal record:
- % proportion of ROH: ratio of total ROH areas to total chromosome
- total extent of ROH: totality of all ROH of a chromosome in relation to its total size
Location and extend of individual ROH are unique for each animal. Due to the randomly occuring recombination, even siblings have variations resulting in differing locations and resulting GIC values.