Genetic Diversity
What is inbreeding?
Inbreeding is currently a topic of significant discussion within the field of animal breeding. Historically, it has been used to enhance specific phenotypic traits such as color However, inbreeding is associated with considerable risks. It diminishes the genetic pool, leading to a reduction in genetic variability that is crucial for the health and robustness of the population. This decreased genetic diversity can elevate the risk of inherited disorders. For instance, the loss of protective alleles can increase susceptibility to diseases. Animals subjected to extensive inbreeding often exhibit reduced lifespan, increased vulnerability to autoimmune disorders, and potential behavioral anomalies. Furthermore, they may experience decreased reproductive success, evident in smaller litter sizes.
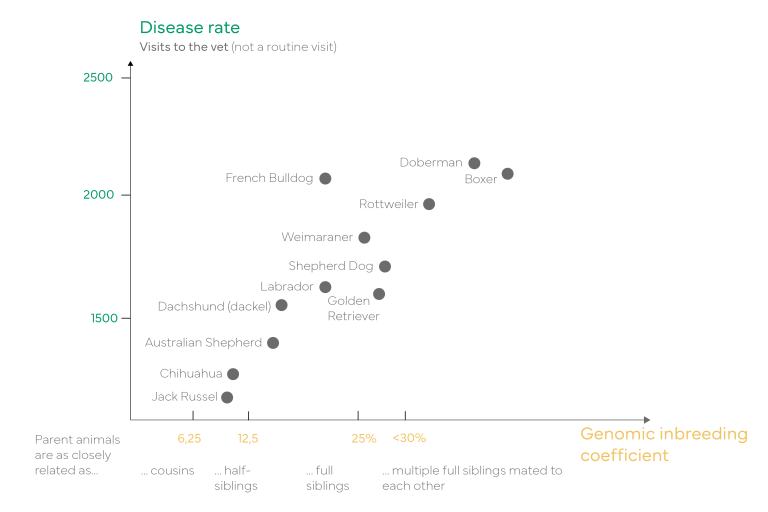
The general fitness of individuals is directly related to their genetic diversity. If an animal is unfit and requires frequent visits to the veterinarian, a high degree of inbreeding may be the reason. The following graph illustrates findings from a recent US study: the correlation between the frequency of unplanned veterinarian visits among specific breeds of dogs and the genomic inbreeding coefficient, which serves as an important measure of inbreeding and genetic diversity.
Number of unplanned veterinarian visits of certain dog breeds in relation to their inbreeding coefficient: Bannasch, D., Famula, T., Donner, J. et al. The effect of inbreeding, body size and morphology on health in dog breeds. Canine Genet Epidemiol 8, 12 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40575-021-00111-4
Is it possible to have a purebred animal without being "overbred"?
When choosing a specific breed for our pets, it is important to be aware the role inbreeding has played in the breed development. The above-mentioned study also shows that, on average, the 227 dog breeds analysed are so strongly inbred that the parents are as closely related as full siblings or even closer. The degree of inbreeding varies among breeds, but not all individuals within these breeds are equally affected. In our own genetic testing, we have identified animals with relatively safe inbreeding values. Utilizing these genetically diverse individuals provides an opportunity for effective breeding management.
Introducing genetic diversity into highly inbred breeds through crossbreeding is challenging but essential. High levels of inbreeding often result in significant health and genetic issues. Therefore, it is necessary to adopt careful and strategic breeding practices to enhance genetic diversity and mitigate the adverse effects of overbreeding.
Effective Tools Against Inbreeding: Selecting Breeding Animals Through Testing
For those seeking to own a purebred dog while ensuring it is not excessively inbred, we provide a comprehensive test that evaluates the key parameters of inbreeding. This test is designed for responsible pet owners, breeding associations committed to addressing the issue of increasing inbreeding within their respective breeds, and breeders who aim to maintain the genetic diversity of their breeding stocks.
Test for Inbreeding & Fitness for dogs
Test for Inbreeding & Fitness for camels
The test evaluates the inbreeding status of an animal using various criteria, including heterozygosity, genomic inbreeding coefficient (GIC), and Runs of Homozygosity (ROH) profile.
Who is this test interesting for?
- Dog owners who are interested in the inbreeding status of their pet.
- Future dog owners seeking a purebred dog while avoiding excessive breeding practices (this applies to mixed breeds as well, as they can also be inbred if the parent animals are closely related).
- Breed clubs aiming to address the issue of progressive inbreeding within their breeds.
- Breeders who want to ensure the genetic diversity of their offspring.
What can I learn from the test?
- The test helps identify animals with low inbreeding values, indicating they are less susceptible to the detrimental effects of inbreeding depression.
- For animals with high inbreeding values, our specialized analysis, utilizing ROH profiles, provides precise information about specific regions within their genetic makeup where inbreeding segments are present. This knowledge enables breeders to select compatible mating partners and employ targeted breeding management to mitigate the negative effects of inbreeding.
- For breeds with a basic inbreeding level of less than 10% Genomic Inbreeding Coefficient (GIC), the test can determine whether high inbreeding values result from direct inbreeding between close relatives (e.g., mother-son, full siblings).
By offering effective solutions for the selection of breeding animals, our test helps safeguard and promote genetic diversity.